Electromyography (EMG): To assess muscle activity.
Electromyography (EMG): A Comprehensive Guide
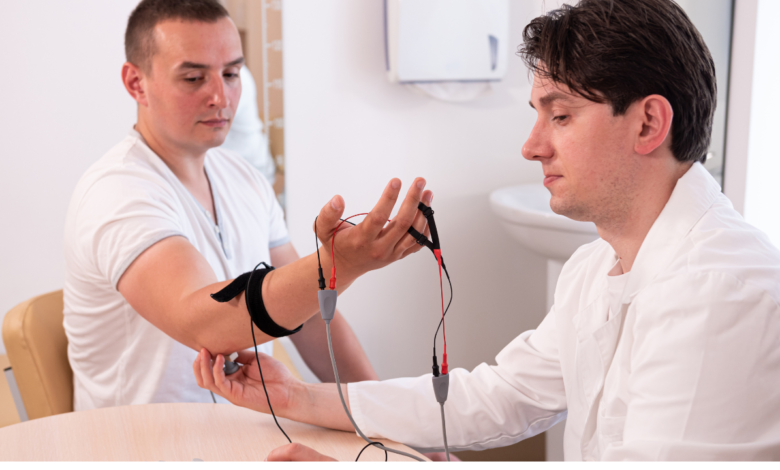
What is Electromyography (EMG)?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the brain. It is used to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions.
Why Electromyography (EMG) is required ?
EEG tests are used for:
- Diagnosing epilepsy: EEG is the primary tool for diagnosing epilepsy, a neurological condition characterized by seizures.
- Evaluating seizures: EEG can help determine the type and location of seizures.
- Monitoring brain activity: EEG can be used to monitor brain activity during sleep, anesthesia, or other procedures.
- Investigating other neurological conditions: EEG can be used to investigate other neurological conditions, such as brain tumors, strokes, and infections.
Which are the method of the Electromyography (EMG) ?
During an EEG test, electrodes are attached to the scalp using a conductive paste. The electrodes record the electrical activity of the brain, which is displayed on a computer screen.
Who should go for the Electromyography (EMG) ?
Individuals who are experiencing seizures, changes in mental status, or other neurological symptoms should consider an EEG test. It may also be recommended for individuals who have undergone brain surgery or have a history of head injuries.
What are the result of the Electromyography (EMG) ?
The results of an EEG test can help to identify abnormal brain activity, such as seizures or other neurological conditions. EEG findings can be used to diagnose and monitor various neurological disorders.
What are the component of this Electromyography (EMG) ?
An EEG test typically involves:
- Attaching electrodes to the scalp
- Recording brain activity
- Analyzing the recorded data





